Areas¶
The application window is always a rectangle on your desktop. It is divided up into a number of re-sizable areas. An area contains the workspace for a particular type of editor, like a 3D View Editor, or an Outliner.
Arranging¶
Blender uses a novel screen-splitting approach to arrange areas. The idea is that you split up that big application window into any number of smaller (but still rectangular) non-overlapping areas. That way, each area is always fully visible, and it is very easy to work in one area and hop over to work in another.
Changing the Size¶
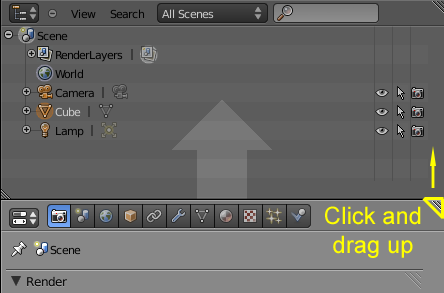
You can resize areas by dragging their borders with LMB.
Simply move your mouse cursor over the border between two areas,
until it changes to a double-headed arrow, and then click and drag.
Splitting and Joining¶
Area Split Widget¶
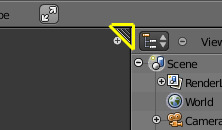
In the upper right and lower left corners of an area are the area split widgets, and they look like a little ridged thumb grip. It both splits and combines areas. When you hover over it, your cursor will change to a cross (✛).
LMB and drag it inward split the area.
You define the direction of that border by either dragging horizontally or vertically.
In order to join two areas LMB click and drag the area splitter outward.
They must be the same dimension (width or height) in the direction you wish to join.
This is so that the combined area space results in a rectangle.
The area that will closed gets a dark overlaid with an arrow. Now you can select the area to be closed by moving the mouse over it.
Release the LMB to complete the join.
If you press Esc or RMB before releasing the mouse, the operation will be aborted.
Area Options¶
RMB on the border opens the Area Options.
- Split Area
- Shows a indicator line that lets you select the area and position where to split.
Tabswitches between vertical/horizontal. - Join Areas
- Shows the join direction overlay.
Confirm or cancel works as described above.
Swapping Contents¶
You can swap the contents between two areas with Ctrl-LMB
on one of the splitters of the initial area, dragging towards the target area,
and releasing the mouse there. The two areas do not need to be side by side,
though they must be inside the same window.
Duplicate Area into new Window¶
Reference
The new window is a fully functional window, which is part of the same instance of Blender. This can be useful, e.g. if you have multiple monitors.
A new window can be created from .
You can also create a new window from an existing area by Shift-LMB
on the area splitter widget, then drag slightly.
The window can be closed with the OS Close Window button.
Toggle Maximize Area¶
Reference
Ctrl-Up, Shift-SpacebarThe maximized area fill the whole application window. It contains the Info Editor and the select area.
You can maximize an area with the
menu entry.
To return to normal size use again menu entry,
or RMB on the editors header and select Maximize Area and
Tiled Area to return.
In the Info Editor header the Back to Previous button on the right of the menus
also returns to tiled areas.
A quicker way to achieve this is to use the shortcuts: Shift-Spacebar,
Ctrl-Down or Ctrl-Up to toggle between maximized and normal areas.
Note
The area your mouse is currently hovering over is the one that will be maximized using the keyboard shortcuts.
Toggle Fullscreen Area¶
Reference
Alt-F10The fullscreen area contains only the main region.
The headers visibility can still be toggled with the shortcut.
To exit the fullscreen move the mouse to the top right corner of the area to reveal the return icon or
use the shortcut Alt-F10.