Fluid Obstacle¶
This object will be used as an obstacle in the simulation. As with a fluid object, obstacle objects currently should not intersect. As for fluid objects, the actual mesh geometry is used for obstacles. For objects with a volume, make sure that the normals of the obstacle are calculated correctly, and radiating properly (use the Flip Normal button, in Edit Mode, Mesh Tools panel, in the Tool shelf), particularly when using a spinned container. Applying a Subdivision Surface Modifier before baking the simulation could also be a good idea if the mesh is not animated.
Options¶
- Volume Initialization Type
- See Volume Initialization Type
- Boundary type
Determines the stickiness of the obstacle surface, called “Surface Adhesion”. Surface Adhesion depends in real-world on the fluid and the graininess or friction/adhesion/absorption qualities of the surface.
- No Slip
- Causes the fluid to stick to the obstacle (zero velocity).
- Free Slip
- Allows movement along the obstacle (only zero normal velocity).
- Part Slip
- Mixes both types, with 0 being mostly no slip, and 1 being identical to free slip.
Note that if the mesh is moving, it will be treated as no slip automatically.
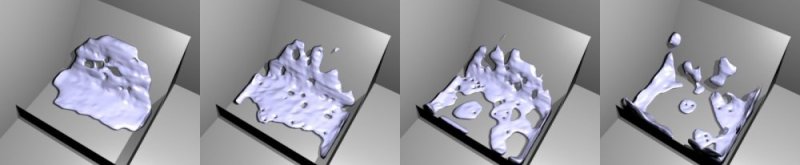
Example of the different boundary types for a drop falling onto the slanted wall. From left to right: no-slip, part-slip 0.3, part-slip 0.7 and free-slip.
- Animated Mesh/Export
- See Animated Mesh/Export
- Part Slip Amount
- Amount of mixing between no- and free-slip, described above.
- Impact Factor
- Amount of fluid volume correction for gain/loss from impacting with moving objects. If this object is not moving, this setting has no effect. However, if it is and the fluid collides with it, a negative value takes volume away from the Domain, and a positive number adds to it. Ranges from -2.0 to 10.0.