Geometry¶
These modifiers have no mix nor influence settings, as they always completely apply to the strokes’ geometry (like object modifiers do). They take the resulting two-dimensional strokes from the Freestyle line set and displace or deform them in various ways.
As with other modifier stacks in Blender, they are applied from top to bottom.
2D Offset¶
The 2D Offset modifier adds some two-dimensional offsets to the stroke backbone geometry. It has two sets of independent options/effects:
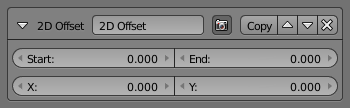
- Start and End
- These two options add the given amount of offset to the start (or end) point of the stroke, along the (2D) normal at those points. The effect is blended over the whole stroke, if you for example, set only Start to 50, the start of the stroke is offset 50 pixels along its normal, the middle of the stroke, 25 pixels along its own normal, and the end point is not moved.
- X and Y
- These two options simply add a constant horizontal and/or vertical offset to the whole stroke.
2D Transform¶
The 2D Transform modifier applies two-dimensional scaling and/or rotation to the stroke backbone geometry. Scale is applied before rotation.
The center (pivot point) of these 2D transformations can be:
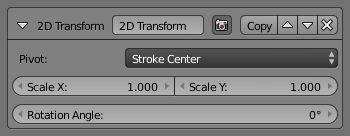
- Stroke Center
- The median point of the stroke.
- Stroke Start
- The beginning point of the stroke.
- Stroke End
- The end point of the stroke.
- Stroke Point Parameter
- The Stroke Point Parameter factor controls where along the stroke the pivot point is (start point if set to 0.0; end point if set to 1.0).
- Absolute 2D Point
The Pivot X and Pivot Y allows you to define the position of the pivot point in the final render (from the bottom left corner).
Important
Currently, you have to take into account the real render size, i.e. resolution and resolution percentage.
- Scale X and Scale Y
- The scaling factors, in their respective axes.
- Rotation Angle
- The rotation angle.
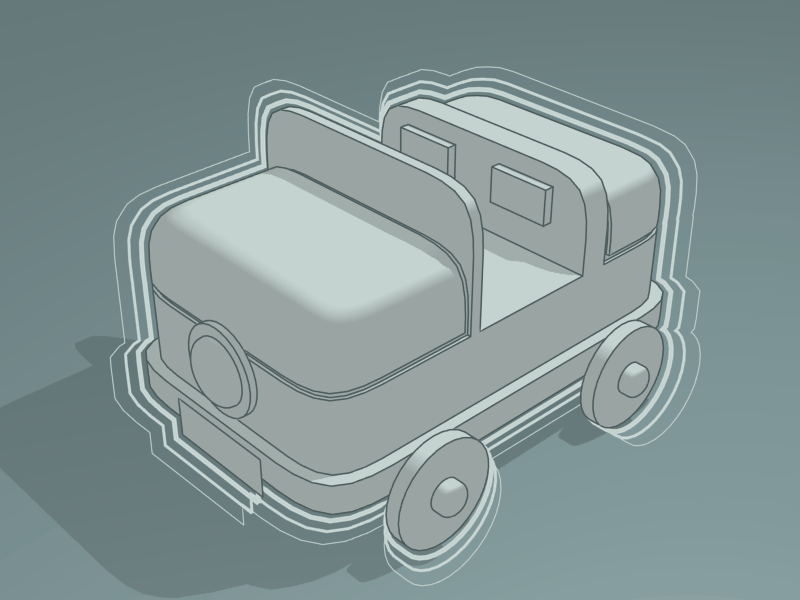
2D Transform modifier File:Toycar_Three_Contours.zip.
Backbone Stretcher¶

The Backbone Stretcher modifier stretches (adds some length to) the beginning and end of the stroke.
- Backbone Length
- Length to add to the strokes’ ends.
Bézier Curve¶
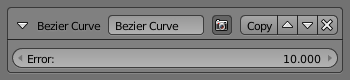
The Bézier Curve modifier replaces the stroke by a Bézier approximation of it.
- Error
- The maximum distance allowed between the new Bézier curve and the original stroke.
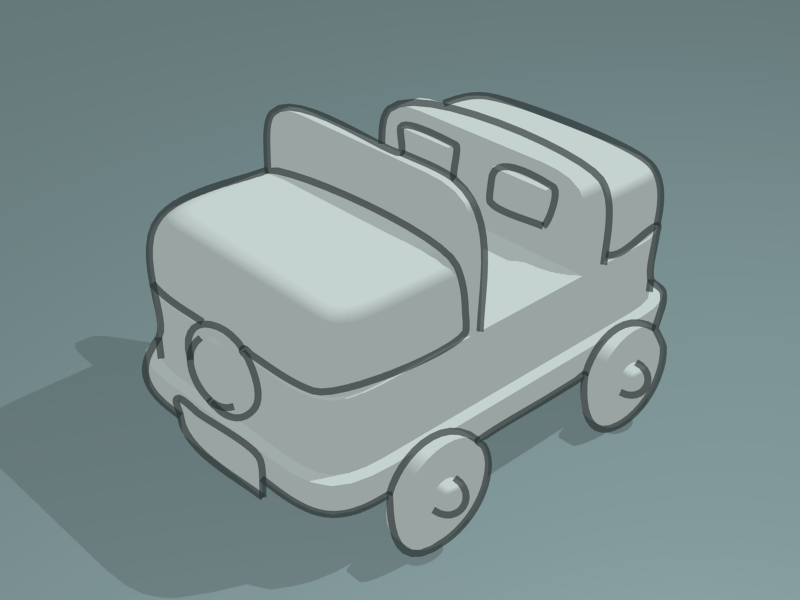
Bézier Curve modifier demo by T.K. File:toycar_bezier.zip.
Blueprint¶
The Blueprint modifier produces blueprint-like strokes using either circular, elliptical, or square contours. A blueprint here refers to those lines drawn at the beginning of free-hand drawing to capture the silhouette of objects with a simple shape such as circles, ellipses and squares.
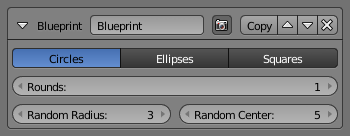
- Shape
- Which base shapes to use for this blueprint: Circles, Ellipses or Squares.
- Rounds
- How many rounds are generated, as if the pen draws the same stroke several times (i.e. how many times the process is repeated).
- Random Radius and Random Center
- For the Circles and Ellipses shapes. Adds some randomness to each round in the relevant aspect. Using more than one round with no randomness would be meaningless, as they would draw over each other exactly.
- Backbone Length and Random Backbone
- For the Squares shapes. The first adds some extra length to each edge of the generated squares (also affected by the second parameter). The second adds some randomness to the squares.
Note that the Min 2D Length feature from the Strokes settings is quite handy here, to avoid the noise generated by small strokes...
Guiding Lines¶
The Guiding Lines modifier replaces a stroke by a straight line connecting both of its ends.
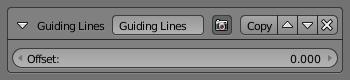
- Offset
- Offset the start and end points along the original stroke, before generating the new straight one.
This modifier will produce reasonable results when strokes are short enough, because shorter strokes are more likely to be well approximated by straight lines. Therefore, it is recommended to use this modifier together with one of the splitting options (by 2D angle or by 2D length) from the Strokes panel.
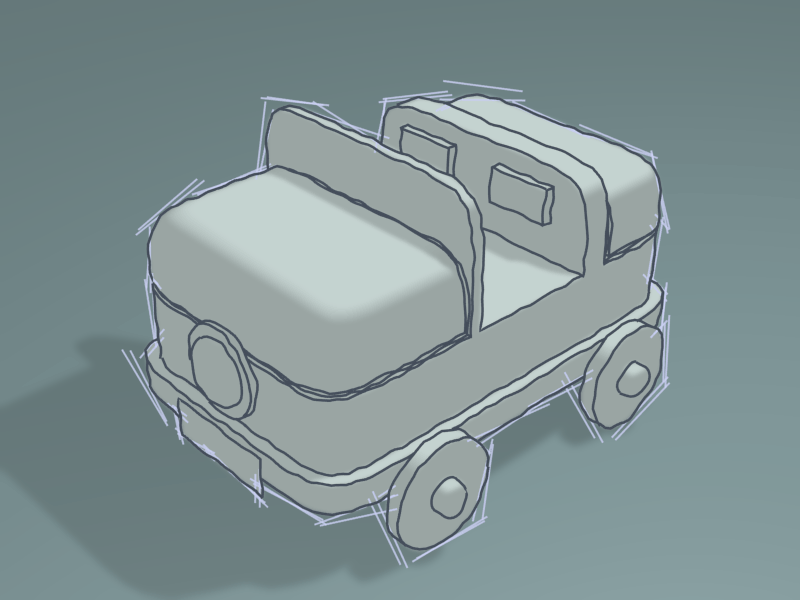
Guiding Lines modifier Demo by T.K. File:Toycar_Guiding_Line.zip.
Perlin Noise 1D¶
The Perlin Noise 1D modifier adds one-dimensional Perlin noise to the stroke. The curvilinear abscissa (value between 0 and 1 determined by a point’s position relative to the first and last point of a stroke) is used as the input to the noise function to generate noisy displacements.
This means that this modifier will give an identical result for two strokes with the same length and sampling interval.
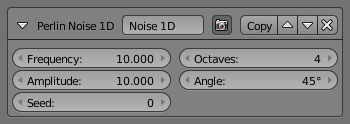
- Frequency
- How dense the noise is (kind of a scale factor along the stroke).
- Amplitude
- How much the noise distorts the stroke in the Angle direction.
- Seed
- The seed of the random generator (the same seed over a stroke will always give the same result).
- Octaves
- The “level of detail” of the noise.
- Angle
- In which direction the noise is applied (0.0 is fully horizontal).
Perlin Noise 2D¶
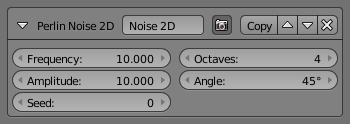
The Perlin Noise 2D modifier adds one-dimensional Perlin noise to the stroke. The modifier generates noisy displacements using 2D coordinates of stroke vertices as the input of the noise generator.
Its settings are exactly the same as the Perlin Noise 1D modifier.
Polygonization¶
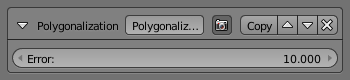
The Polygonization modifier simplifies strokes as much as possible (in other words, it transforms smooth strokes into jagged polylines).
- Error
- The maximum distance allowed between the new simplified stroke and the original one (the larger this value is, the more jagged/approximated the resulting polylines are).
Sampling¶
The Sampling modifier changes the definition, precision of the stroke, for the following modifiers.
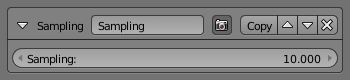
- Sampling
- The smaller this value, the more precise are the strokes. Be careful; too small values will require a huge amount of time and memory during render!
Simplification¶
The Simplification modifier merges stroke vertices that lie close to one another, like the Decimate modifier for meshes.

- Tolerance
- Measure for how close points have to be to each other to be merged. A higher tolerance means more vertices are merged.
Sinus Displacement¶
The Sinus Displacement modifier adds a sinusoidal displacement to the stroke.
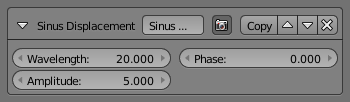
- Wavelength
- How wide the undulations are along the stroke.
- Amplitude
- How high the undulations are across the stroke.
- Phase
- Allows “offsetting” (“moving”) the undulations along the stroke.
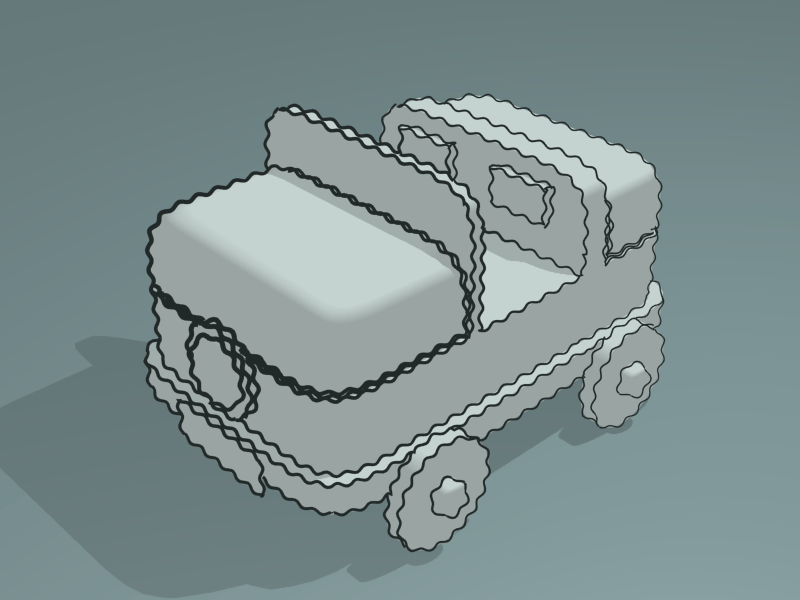
Sinus Displacement modifier demo by T.K. File:Toycar_Sinus.zip.
Spatial Noise¶
The Spatial Noise modifier adds some spatial noise to the stroke. Spatial noise displacements are added in the normal direction (i.e., the direction perpendicular to the tangent line) evaluated at each stroke vertex.
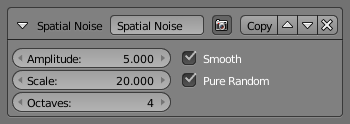
- Amplitude
- How much the noise distorts the stroke.
- Scale
- How wide the noise is along the stroke.
- Octaves
- The level of detail of the noise.
- Smooth
- When enabled, apply some smoothing over the generated noise.
- Pure Random
- When disabled, the next generated random value depends on the previous one; otherwise they are completely independent. Disabling this setting gives a more “consistent” noise along a stroke.
Tip Remover¶
The Tip Remover modifier removes a piece of the stroke at its beginning and end.
- Tip Length
- Length of stroke to remove at both of its tips.