Render Layers and Passes¶
Layers¶
Reference
This section covers only the Render Layer settings appropriate for the Blender Render engine. For the engine-independent settings, see this section.
- Exclude
- Scene layers are shared between all render layers; however, sometimes it is useful to leave out some object influence for a particular render layer. That is what this option allows you to do.
- Material
- Overrides all materials in the render layer.
- Samples
- Render layer samples to override the scene samples. Controlled by the layer samples in the sampling panel.
- Use Environment
- Disables rendering the Environment render pass in the final render.
- Use AO
- Disables rendering the Ambient Occlusion render pass in the final render.
- Use Surfaces
- Disables rendering object materials in the final render.
- Use Hair
- Disables rendering hair strands in the final render.
Passes¶
Reference
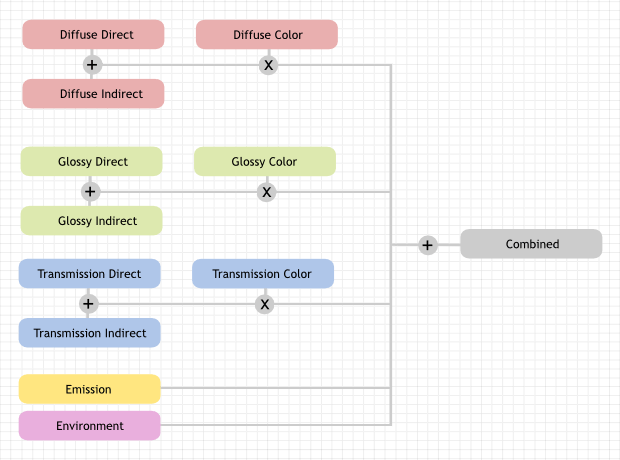
Passes can be used to split rendered images into colors, direct and indirect light to edit them individually, and also to extract data such as depth or normals.
Lighting Passes¶
- Diffuse Direct
- Direct lighting from diffuse BSDFs. We define direct lighting as coming from lamps, emitting surfaces, the background, or ambient occlusion after a single reflection or transmission off a surface. BSDF color is not included in this pass.
- Diffuse Indirect
- Indirect lighting from diffuse BSDFs. We define indirect lighting as coming from lamps, emitting surfaces or the background after more than one reflection or transmission off a surface. BSDF color is not included in this pass.
- Diffuse Color
- Color weights of diffuse BSDFs. These weights are the color input socket for BSDF nodes, modified by any Mix and Add Shader nodes.
- Glossy Direct, Indirect, Color
- Same as above, but for glossy BSDFs.
- Transmission Direct, Indirect, Color
- Same as above, but for transmission BSDFs.
- Subsurface Direct, Indirect, Color
- Same as above, but for subsurface BSDFs.
- Emission
- Emission from directly visible surfaces.
- Environment
- Emission from the directly visible background. When the film is set to transparent, this can be used to get the environment color and composite it back in.
- Shadow
- Shadows from lamp objects. Mostly useful for compositing objects with shadow into existing footage.
- Ambient Occlusion
- Ambient occlusion from directly visible surfaces. BSDF color or AO factor is not included; i.e. it gives a ‘normalized’ value between 0 and 1.
Note
Transparent BSDFs are given special treatment. A fully transparent surface is treated as if there is no surface there at all; a partially transparent surface is treated as if only part of the light rays can pass through. This means it is not included in the Transmission passes; for that a glass BSDF with index of refraction 1.0 can be used.
Data Passes¶
- Combined
- The final combination of render passes with everything included.
- Z
Distance in BU to any visible surfaces.
Note
The Z pass only uses one sample. When depth values need to be blended in case of motion blur or DOF, use the mist pass.
- Mist
- Distance to visible surfaces, mapped to the 0.0-1.0 range. When enabled, settings are in World tab. This pass can be used in compositing to add fade out object that are further away.
- Normal
- Surface normal used for shading.
- Vector
- Motion vectors for the vector blur node. The four components consist of 2D vectors giving the motion towards the next and previous frame position in pixel space.
- UV
- Default render UV coordinates.
- Object Index
- Creates a mask of the object that can be later read by the ID Mask Node in the compositor.
- Material Index
- Creates a mask of the material that can be later read by the ID Mask Node in the compositor.
Note
The Z, Object Index and Material Index passes are not anti-aliased.
- Alpha Threshold
- Z, Index, normal, UV and vector passes are only affected by surfaces with alpha transparency equal to or higher than this threshold. With value 0.0 the first surface hit will always write to these passes, regardless of transparency. With higher values surfaces that are mostly transparent can be skipped until an opaque surface is encountered.