Material Node¶
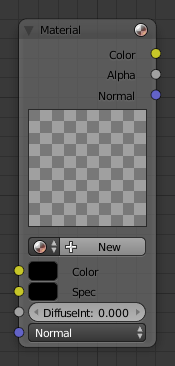
Material node.
The Material node is used for shading.
Inputs¶
- Color
- The diffuse color or texture.
- Specular
- The specular color or texture that is reflected as the point of view get perpendicular to the light source reflecting off the surface.
- Diffuse Intensity
- Amount of diffuse scattering. Can also be set by a texture.
- Normal
- Standard normal input. Used for normal mapping.
Note
Normal Override
The normal input socket does not blend the source normal with the underlying geometry but completely overrides the normals.
Properties¶
- Material field
- Can be used to browse and select materials.
- Diffuse
- De/activate diffuse shading.
- Specular
- De/activate specular shading.
- Invert Normal
- Inverts the material input normal when activated. (which, is a combination of the 3D normal given to it by the 3D object plus the normal input point).
Outputs¶
- Color
- Shaded color value.
- Alpha
- Alpha transparency value.
- Normal
- Direction of the normal.
Examples¶
Using the Material Node with Specularity¶
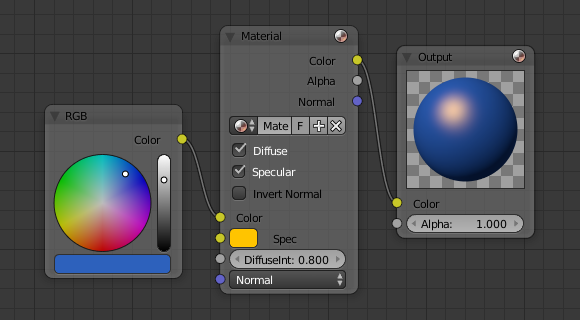
Material Node using Specularity.
To make a material node actually generate a color, at least a basic input color have to be specified, and optionally a specularity color. The specularity color is the color that shines under intense light.
For example, consider the mini-map to the right. The base color, a dark blue, is connected from an RGB color generator node to the Color input socket. The specular color, yellow, is connected to the Spec input. Under Normal lighting conditions on a flat surface, this material will produce a deep blue color and, as the point of view approaches a spot perpendicular to the light, the yellow specular color mix in becomes visible.
Note
Enable Spec
To see specularity, the specular toggle has to be enabled, which is located just below the material color button in the node.